Introduction

When understanding engine blocks, it's essential to recognize their role as the foundation of an engine, housing crucial components and providing structural support. The materials used in engine blocks play a significant role in their performance and durability, making them a key consideration in manufacturing. Additionally, the importance of engine bracket mounting cannot be overlooked, as it ensures proper alignment and support for various engine components.
Understanding Engine Blocks
An engine block is the main structure of an internal combustion engine, housing cylinders, coolant passages, and other essential components. It is the foundation for the entire engine assembly, providing support and alignment for various moving parts. Understanding the intricacies of engine blocks is crucial for designing efficient and reliable engines.
Engine blocks are typically made from cast iron or aluminum, with each material offering advantages and disadvantages. Cast iron engine blocks are known for their durability and resistance to wear, making them a popular choice for heavy-duty applications. On the other hand, aluminum engine blocks are lighter in weight, which can improve fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Understanding the properties of these materials is essential for selecting the most suitable option based on the specific requirements of the engine design.
Materials Used in Engine Blocks
The material used for an engine block significantly influences its performance and efficiency. Common materials include cast iron, aluminum, and steel, each with distinct advantages.
- Cast iron: is renowned for its exceptional strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- Aluminum: offers a lightweight option to enhance fuel efficiency and vehicle handling.
- Steel: balances strength and weight and is suitable for a wide range of engines.
Ultimately, the optimal material depends on the specific requirements of the engine and its intended use.
Importance of Engine Bracket Mounting
Proper bracket mounting is crucial for securing various components within the engine block assembly. It ensures that critical parts such as cylinder heads and crankshafts are securely held, preventing potential damage or misalignment during operation.
Proper bracket mounting also plays a role in maintaining the engine's overall balance and stability, which is essential for smooth and efficient operation. Securely fastening components helps minimize vibrations and reduce the risk of premature wear and tear on vital engine parts. This, in turn, contributes to the engine's longevity and reliability, ultimately saving on maintenance costs and ensuring optimal performance.
What Is an Engine Block?

Definition and Function
An engine block is the main structure of an internal combustion engine, housing the cylinders and providing passages for coolant and lubrication. It also serves as the mounting point for other engine components, such as the cylinder head, crankshaft, and pistons.
The evolution of engine blocks has seen significant advancements over the years, with manufacturers constantly seeking to improve performance and efficiency. Early engine blocks were typically cast iron, but modern designs often utilize aluminum or composite materials to reduce weight and improve thermal efficiency. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing techniques, such as CNC machining, have allowed for more complex and precise designs, resulting in better engine performance.
Evolution of Engine Blocks
The evolution of engine blocks has seen a shift from cast iron to aluminum due to its lightweight properties and better heat dissipation. This transition has allowed for more efficient and powerful engines while reducing overall vehicle weight for improved fuel economy.
Using aluminum in engine blocks has also led to advancements in manufacturing processes, allowing for more complex and intricate designs to be created. This has resulted in engines that are more powerful, efficient, and compact, taking up less space under the hood. As a result, vehicles have become smaller and sleeker while maintaining high-performance standards.
Common Materials Used
Engine blocks are commonly made from cast iron or aluminum alloys due to their strength, durability, and heat resistance. Cast iron is known for its high compression strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications such as truck engines.
Engine blocks made from aluminum alloys are favored for their lightweight properties, which can improve fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Aluminum also has excellent heat dissipation properties, making it suitable for high-performance engines in sports cars and racing vehicles. Additionally, aluminum is more corrosion-resistant than cast iron, prolonging the lifespan of the engine block and reducing maintenance costs.
Engine Bracket Mounting

When it comes to engine assembly, mounting engine brackets play a crucial role in ensuring proper alignment and support for various engine components. The bracket mounting also helps absorb vibrations and shocks, which are essential for the engine's smooth operation.
Importance in Engine Assembly
The importance of engine bracket mounting cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the engine's overall performance and longevity. Properly mounted brackets ensure that all components are securely placed, preventing unnecessary movement or damage during operation.
Types of Engine Bracket Mounting
Several types of engine bracket mounting systems are used in manufacturing, including bolt-on brackets, weld-on brackets, and integrated mounting points within the engine block itself. Each type is designed to accommodate specific engineering requirements and assembly processes.
Materials Used for Bracket Mounting
Engine brackets can be made from various materials, including steel, aluminum, and cast iron. The choice of material depends on factors such as strength requirements, weight considerations, and compatibility with other components within the engine assembly.
Engine Block Materials
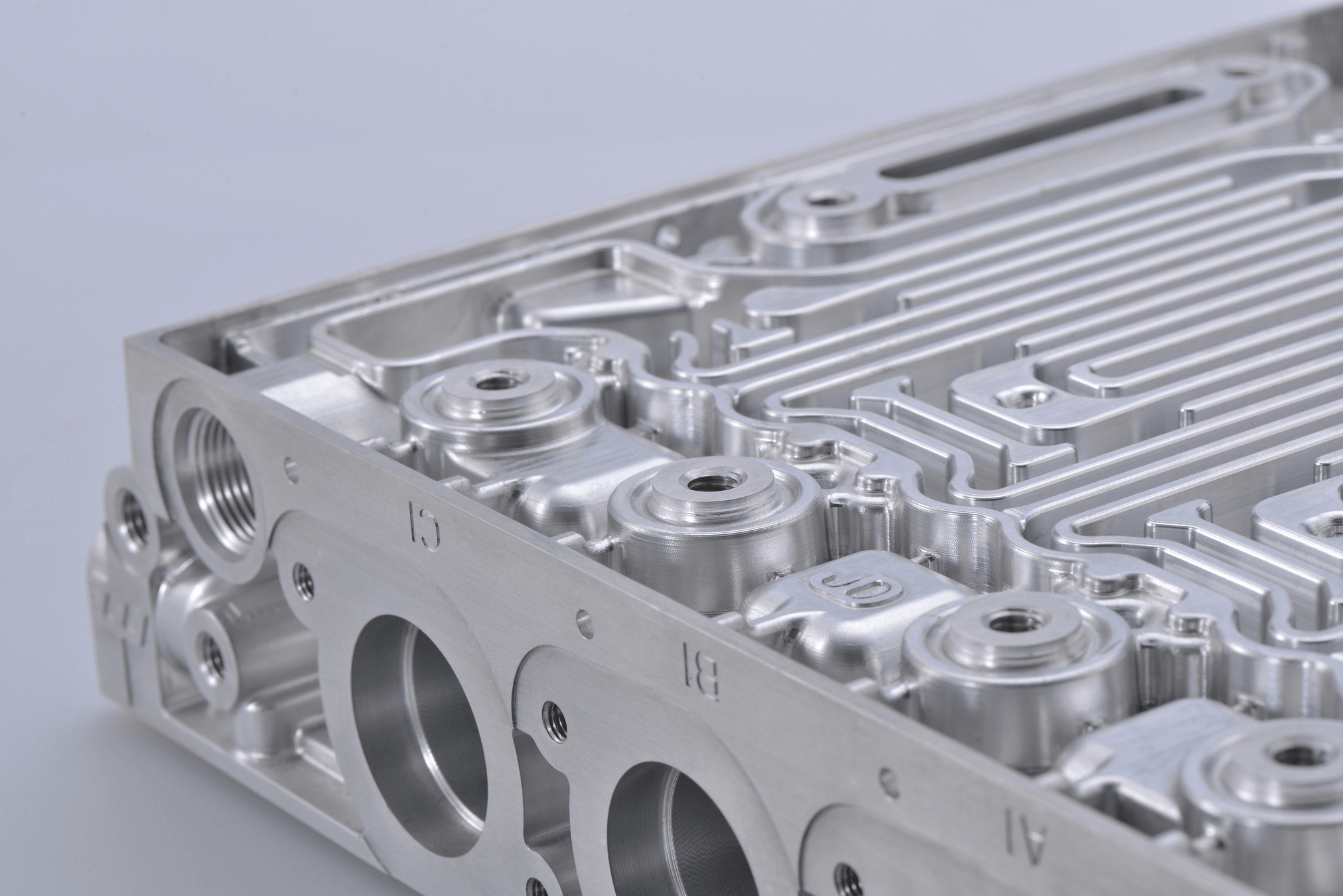
When it comes to engine block materials, there are several options available, each with its unique properties and benefits. The most common materials used for engine blocks are cast iron, aluminum, and steel. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and heat resistance, making them ideal for withstanding extreme conditions within an engine.
Cast Iron Engine Blocks
Cast iron has been a popular choice for engine blocks for many years due to its excellent heat dissipation and high tensile strength. Engines made of cast iron are known for their durability and resistance to wear and tear, making them a reliable choice for heavy-duty applications such as trucks and industrial machinery.
Aluminum Engine Blocks
Aluminum engine blocks have gained popularity recently due to their lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. This material is ideal for high-performance engines, such as sports cars and aircraft engines, where weight reduction is crucial. Additionally, aluminum's corrosion resistance makes it a durable choice for various applications.
Steel Engine Blocks
Steel engine blocks offer exceptional strength and rigidity, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications where durability is paramount. While steel is heavier than aluminum, it provides superior resistance to deformation under high pressure or temperature conditions, making it an excellent choice for engines in large vehicles or industrial equipment.
By understanding the unique properties of each material used in engine blocks—cast iron, aluminum, and steel—manufacturers can make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable material based on the application's specific requirements.
Engine Block Manufacturing Process

The manufacturing process of engine blocks involves several crucial steps to ensure the quality and performance of the final product. One of the key aspects is the use of die-casting molds, which are essential for shaping and forming the engine blocks. These molds are carefully designed to create precise and accurate castings that meet the required specifications.
Die-Casting Molds
Die-casting molds are typically made from high-quality steel or other durable materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressure during casting. These molds play a critical role in determining the engine blocks' final shape, dimensions, and surface finish. The design and construction of these molds require meticulous attention to detail to ensure consistent and reliable production.
Die-casting molds are typically made from high-quality steel or other durable materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressure during casting. These molds play a critical role in determining the engine blocks' final shape, dimensions, and surface finish. The design and construction of these molds require meticulous attention to detail to ensure consistent and reliable production. Additionally, technological advancements have led to the development of innovative cooling systems within the die-casting molds, allowing for more efficient heat dissipation and faster production cycles. This has significantly improved productivity and reduced manufacturing costs for engine block production.
Aluminum and Zinc Castings
Engine blocks are commonly made from aluminum or zinc alloys due to their lightweight nature, excellent thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. The casting process involves melting these metals and pouring them into the die-casting molds to form the desired shapes. This method allows for intricate designs and complex geometries to be achieved precisely, making it a preferred choice for engine block manufacturing.
Surface Treatment
Engine blocks undergo surface treatments to optimize their performance and longevity. These processes enhance the block's durability, appearance, and overall quality.
The following treatments are commonly applied to engine blocks:
- Heat treatment: Improves mechanical properties like strength and hardness.
- Machining: Achieves precise dimensions and surface finish for optimal sealing.
- Coating: Protects against corrosion and reduces friction.
- Finishing: Enhances the block's aesthetic appeal.
By carefully selecting and applying these treatments, manufacturers can produce engine blocks that meet the highest performance and reliability standards.
Engine Block Applications

Engine blocks are an essential component in the automotive industry and are crucial for the production of various automotive parts. From cylinder heads to crankshafts, engines made of cast iron and aluminum are widely used in vehicle manufacturing. The durability and strength of these materials make them ideal for withstanding the high temperatures and pressures within an engine.
Automotive Parts
Engine blocks are vital in producing automotive parts such as cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, and engine brackets. These components are crucial for ensuring the efficient performance and longevity of vehicles. With technological advancements, manufacturers constantly innovate to improve the quality and reliability of engine blocks for automotive applications.
Gas Appliance Parts
In addition to automotive applications, engine blocks made from cast iron and aluminum are used to manufacture gas appliance parts. These durable materials, from burners to valves, provide the strength and heat resistance required for gas appliances to function effectively and safely.
Power Tool Parts
Furthermore, engine blocks find applications in power tool manufacturing, where their robustness is essential for withstanding heavy-duty operations. Components such as motor housings and gear cases benefit from the durability and stability of cast iron and aluminum engine blocks.
Importance of Engine Blocks in Manufacturing

Engine blocks are crucial components in manufacturing as they serve as the foundation for internal combustion engines. These blocks house the cylinders, crankshaft, and other key components, providing structural support and ensuring the engine's proper functioning.
Advantages of Different Engine Block Materials
The choice of material for an engine block significantly impacts its performance and durability. Iron, aluminum, and steel are commonly used, each with distinct advantages.
- Cast iron: Renowned for its durability and resistance to wear and tear.
- Aluminum: Highly valued for its lightweight properties and exceptional heat dissipation.
- Steel: Offers a balance between durability and weight, making it suitable for high-performance engines. It also excels in corrosion resistance.
Advancements in metallurgy have made steel engine blocks a reliable choice for various automotive applications.
Buttler's Contribution to Engine Block Technology
Ningbo Buttler Precision Machinery Co., Ltd. has significantly contributed to engine block technology through its expertise in die-casting molds and surface treatment processes. Their innovative tooling designs have helped optimize parts for cost-effective manufacturing and improved casting quality.
Ningbo Buttler Precision Machinery Co., Ltd. has also been at the forefront of developing environmentally friendly surface treatment processes for engine blocks. By utilizing sustainable materials and refining their manufacturing techniques, Buttler has reduced the environmental impact of their production while maintaining high-quality standards. This commitment to eco-friendly practices benefits the planet and aligns with the industry's increasing focus on sustainability.

